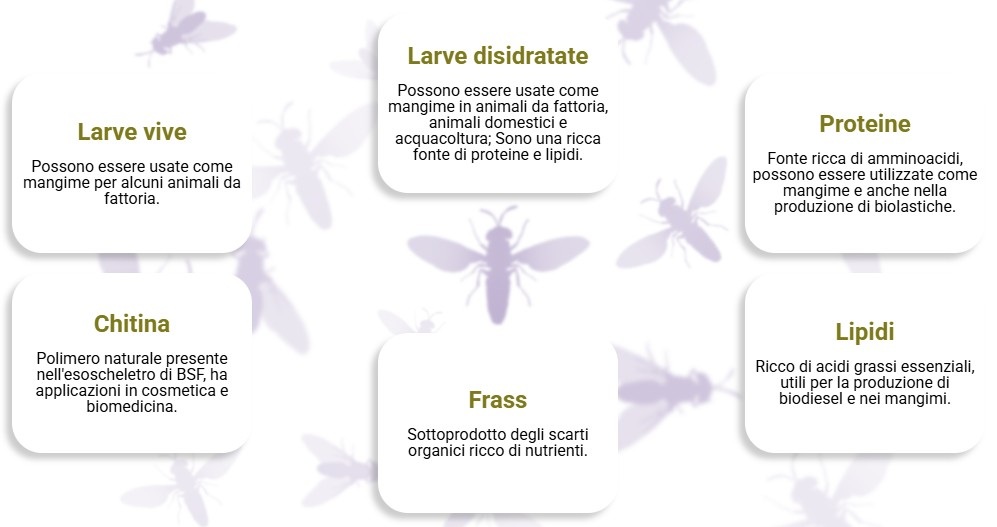
La produzione di larve di Hermetia illucens è solo una piccola parte del potenziale che questo insetto può esprimere. Dall’allevamento delle larve si ottengono due prodotti: le larve stesse e il frass.
Le larve vive oppure congelate o disidratate possono essere utilizzate direttamente per l’alimentazione di parecchi animali allevati, come pesci, polli, uccelli e rettili, oppure essere trasformate in farine utilizzate per la formulazione di mangimi.
Direttamente dalle larve si ottengono:
Dal ciclo di produzione delle larve si ottiene il frass, che, pur essendo un prodotto di scarto del processo di allevamento delle larve, è un mix di scarti organici (substrato che è stato dato alle larve per alimentarsi ed escrementi prodotti dalle larve) ancora ricco di nutrienti facilmente disponibili e quindi rappresenta un concime per le piante o ammendante, utilizzabile in agricoltura.
Abd El‐Hack, M.E., Shafi, M.E., Alghamdi, W.Y., Abdelnour, S.A., Shehata, A.M., Noreldin, A.E., Ashour, E.A., Swelum, A.A., Al‐sagan, A.A., Alkhateeb, M., Taha, A.E., Abdel‐moneim, A.M.E., Tufarelli, V., Ragni, M., 2020. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) meal as a promising feed ingredient for poultry: A comprehensive review. Agriculture (Switzerland).
https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10080339
Barragan-Fonseca, K.B., Dicke, M., van Loon, J.J.A., 2017. Nutritional value of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and its suitability as animal feed - a review. J Insects Food Feed.
https://doi.org/10.3920/jiff2016.0055
Candian, V., Meneguz, M., Tedeschi, R., 2023. Immune responses of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) reared on catering waste. Life 13.
https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010213
Elhag, O., Zhang, Y., Xiao, X., Cai, M., Zheng, L., Jordan, H.R., Tomberlin, J.K., Huang, F., Yu, Z., Zhang, J., 2022. Inhibition of zoonotic pathogens naturally found in pig manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae and their intestine bacteria. Insects 13.
https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010066
Ipema, A.F., Gerrits, W.J.J., Bokkers, E.A.M., Kemp, B., Bolhuis, J.E., 2021. Live black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) provisioning is a promising environmental enrichment for pigs as indicated by feed- and enrichment-preference tests. Appl Anim Behav Sci 244.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2021.105481
Kariuki, E.G., Kibet, C., Paredes, J.C., Mboowa, G., Mwaura, O., Njogu, J., Masiga, D., Bugg, T.D.H., Tanga, C.M., 2023. Metatranscriptomic analysis of the gut microbiome of black soldier fly larvae reared on lignocellulose-rich fiber diets unveils key lignocellulolytic enzymes. Front Microbiol 14.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1120224
Leong, S.Y., Kutty, S.R.M., Bashir, M.J.K., Li, Q., 2021. A circular economy framework based on organic wastes upcycling for biodiesel production from Hermetia illucens. Engineering Journal 25, 223–234.
https://doi.org/10.4186/ej.2021.25.2.223
Ma, C., Huang, Z., Feng, X., Memon, F.U., Cui, Y., Duan, X., Zhu, J., Tettamanti, G., Hu, W., Tian, L., 2024. Selective breeding of cold-tolerant black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae: Gut microbial shifts and transcriptional patterns. Waste Management 177, 252–265.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2024.02.007
Mangindaan, D., Kaburuan, E.R., Meindrawan, B., 2022. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) for Biodiesel and/or Animal Feed as a Solution for Waste-Food-Energy Nexus: Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability (Switzerland).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113993
Mapanao, R., Jiwyam, W., Nithikulworawong, N., Weeplian, T., 2023. Effects of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae as a fish meal replacement on growth performance, feed utilisation, morphological characters and carcass composition of Thai climbing perch (Anabas testudineus). Journal of Applied Aquaculture 35, 1–15.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10454438.2021.1923609
Ngalo, S., Mukhebi, A., Otieno, K., 2023. Dogs Owners’ Perception on the Use of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens L (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae as an Alternative
Source of Protein in Dog Food in Kenya. East African Journal of Agriculture and Biotechnology 6, 116–128.
https://doi.org/10.37284/eajab.6.1.1180
Penazzi, L., Schiavone, A., Russo, N., Nery, J., Valle, E., Madrid, J., Martinez, S., Hernandez, F., Pagani, E., Ala, U., Prola, L., 2021. In vivo and in vitro Digestibility of an Extruded Complete Dog Food Containing Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal as Protein Source. Front Vet Sci 8.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.653411
Petkov, E., 2019. Possibilities for the use of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) in poultry breeding as a feed and waste utilization. International Journal of Innovative Approaches in Agricultural Research 3, 529–542.
https://doi.org/10.29329/ijiaar.2019.206.17
Purkayastha, D., Sarkar, S., 2020. Physicochemical structure analysis of chitin extracted from pupa exuviae and dead imago of wild Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). J Polym Environ 28, 445–457.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01620-x
Radzikowska-Kujawska, D., Sawinska, Z., Grzanka, M., Kowalczewski, P.Ł., Sobiech, Ł., Świtek, S., Skrzypczak, G., Drożdżyńska, A., Ślachciński, M., Nowicki, M., 2023. Hermetia illucens frass improves the physiological state of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) and its nutritional value under drought. PLoS One 18.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0280037
Rangel, F., Monteiro, M., Santos, R.A., Ferreira-Martins, D., Cortinhas, R., Gasco, L., Gai, F., Pousão-Ferreira, P., Couto, A., Oliva-Teles, A., Serra, C.R., Enes, P., 2024. Novel chitinolytic Bacillus spp. increase feed efficiency, feed digestibility, and survivability to Vibrio anguillarum in European seabass fed with diets containing Hermetia illucens larvae meal. Aquaculture 579.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740258
Romano, N., Datta, S.N., Sinha, A.K., Pande, G.S.J., 2023. Partially replacing synthetic fertilizer with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae frass enhances kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) production. Technology in Horticulture 3, 0–0.
https://doi.org/10.48130/tih-2023-0008
Romano, N., Islam, S., 2023. Productivity and Elemental/Chlorophyll Composition of Collard Greens in an Aquaponic System at Different Combinations of Media and Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Frass Supplementations. Aquac Res 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3308537
Siddiqui, S.A., Gadge, A.S., Hasan, M., Rahayu, T., Povetkin, S.N., Fernando, I., Castro-Muñoz, R., 2024. Future opportunities for products derived from black soldier fly (BSF) treatment as animal feed and fertilizer - A systematic review. Environ Dev Sustain.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04673-8
Spranghers, T., Michiels, J., Vrancx, J., Ovyn, A., Eeckhout, M., De Clercq, P., De Smet, S., 2018. Gut antimicrobial effects and nutritional value of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) prepupae for weaned piglets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 235, 33–42.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.08.012
Sultana, A., Luo, H., Ramakrishna, S., 2021. Harvesting of antimicrobial peptides from insect (Hermetia illucens) and its applications in the food packaging. Applied Sciences (Switzerland).
https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156991
Tahamtani, F.M., Ivarsson, E., Wiklicky, V., Lalander, C., Wall, H., Rodenburg, T.B., Tuyttens, F.A.M., Hernandez, C.E., 2021. Feeding live Black Soldier Fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) to laying hens: effects on feed consumption, hen health, hen behavior, and egg quality. Poult Sci 100.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.101400
Ulumiah, M., Lamid, M., Pursetyo, K.T., 2021. Substitution of commercial feed with maggot meal (Hermetia illucens) to the growth rate, feed conversion ratio and feed efficiency catfish (Pangasius pangasius), in: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing Ltd.
Hermetia illucens, specie comunemente conosciuta come Black Soldier Fly (BSF), è un insetto innocuo per l’uomo, fa parte dell’ordine dei Ditteri e della famiglia degli Straziomidi. Vive in ambienti caldi, è originaria dei climi tropicali, ma ha ormai colonizzato spontaneamente anche aree temperate, come l’Italia.
Nota fino a pochi anni fa solo in ambito forense, negli ultimi dieci anni è stata oggetto di numerosissime ricerche, grazie alla sua notevole capacità di sfruttare materiali organici di varia tipologia, trasformandoli in prodotti di alto valore come proteine, lipidi, chitina etc. Di particolare interesse perché in grado di nutrirsi di materiali di scarto derivanti da altri processi di trasformazione.
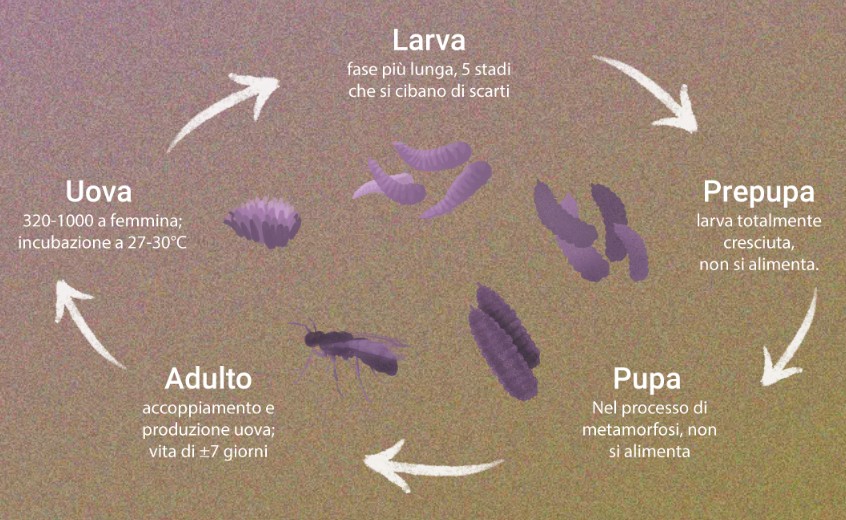
Il suo ciclo di vita dura complessivamente circa 40 giorni, dalla schiusa delle uova si ottengono le larve (sviluppo postembrionale olometabolo) che, attraverso 5 età e in circa 15 giorni, se le condizioni sono ottimali, raggiungono la maturità per poi trasformarsi in pupa, stadio in cui l’insetto non si muove e non si nutre, in cui avvengono profonde trasformazioni che permettono il completamento della metamorfosi con lo sfarfallamento dell’adulto.
I parametri ottimali per uno sviluppo dell’insetto rapido ed efficiente sono 27 °C di temperatura e 65% circa di umidità relativa. La larva è molto vorace, in grado di accrescere velocemente e di sfruttare tutti i substrati organici in decomposizione, contenenti un minimo di sostanze nutritive, sia di derivazione vegetale, sia animale. Le larve mature possono essere utilizzate per molti scopi, primo fra tutti la produzione di mangimi per animali allevati. Dall’allevamento delle larve si ottiene uno scarto, tecnicamente un letame, ricco di azoto, fosforo e potassio, utile come concime e ammendante in agricoltura. Questo prodotto, chiamato frass, è costituito dagli scarti su cui si sono alimentate le larve ma che non hanno del tutto ingerito e gli escrementi prodotti durante il periodo di alimentazione delle larve.
Abd El-Hack, M., Shafi, M., Alghamdi, W., Abdelnour, S., Shehata, A., Noreldin, A., Ashour, E., Swelum, A., Al-Sagan, A., Alkhateeb, M., Taha, A., Abdel-Moneim, A.-M., Tufarelli, V., Ragni, M., 2020. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Meal as a Promising Feed Ingredient for Poultry: A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture 10, 339.
Guilliet, J., Baudouin, G., Pollet, N., Filée, J., 2022. What complete mitochondrial genomes tell us about the evolutionary history of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens. BMC Ecol Evol 22, 72.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-022-02025-6
Leong, S.Y., Kutty, S.R.M., 2020. Characteristic of Hermetia illucens Fatty Acid and that of the Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Synthesize Based on Upcycling of Perishable Waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 11, 5607–5614.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01018-0
Lomonaco, G., Franco, A., De Smet, J., Scieuzo, C., Salvia, R., Falabella, P., 2024. Larval Frass of Hermetia illucens as Organic Fertilizer: Composition and Beneficial Effects on Different Crops. Insects 15, 293.
https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15040293
Lu, S., Taethaisong, N., Meethip, W., Surakhunthod, J., Sinpru, B., Sroichak, T., Archa, P., Thongpea, S., Paengkoum, S., Purba, R.A.P., Paengkoum, P., 2022. Nutritional Composition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and Its Potential Uses as Alternative Protein Sources in Animal Diets: A Review. Insects 13, 831.
https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13090831
Martínez-Sánchez, A., Magaña, C., Saloña, M., Rojo, S., 2011. First record of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) on human corpses in Iberian Peninsula. Forensic Sci Int 206, e76–e78.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.10.021
Nguyen, T.T.X., Tomberlin, J.K., Vanlaerhoven, S., 2015. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ Entomol 44, 406–410
https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/nvv002
Rajasekar, B., Naga Harshitha, D., Mishra, P., Hudge, B. V, Navya Swetha, T., 2023. A review on black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens as a potential source for organic waste management. ~ 3469 ~ The Pharma Innovation Journal 12, 3469–3474.
Tomberlin, J.K., van Huis, A., 2020. Black soldier fly from pest to ‘crown jewel’ of the insects as feed industry: an historical perspective. J Insects Food Feed 6, 1–4.